
I take a chip daily as a matter of course. amusingly, ginseng is added to the base of an awful lot of pharmaceuticals, i believe to moderate any side effects. Who knew?
I do conjecture that ginseng acts to properly balance your blood chemistry which is often disturbed by menopause and pharmaceuticals.
Forty years ago, I had a small part to play in introducing Ginseng cultivation into British Columbia and found almost nothing in hte literature. so bad that an informant told me that superstious old folks used it. Obviously, this is no longer true. At the time i identified it as a good base for meds. that happened but without fan fare.
My wife was prescribed VIOXX and then suffered greatly for months even after she stopped it. Ginseng ended all the side effects.
So here we are with a wall of science to support it.
Ginseng, the King of All Medicinal Herbs–6 Major Functions, Therapeutic Prescriptions, and Contraindications
Used properly, ginseng supports the heart, vision, mood, cognition, and even promotes longevity.Ginseng serves multipurposes such as invigorating the central nervous system, improving cardiovascular function, and treating cancer. (Jinning Li/Shutterstock)
8/31/2023Updated:
Health Viewpoints
Panax Ginseng, true to the root meaning of its name, is a panacea of health benefits. Panax ginseng, in Greek, means "all-healing" and shares the same origin as "panacea." Modern medicine has confirmed the many benefits of ginseng, including improving heart and brain function and treating cancer.
You may be aware that Ginseng can be taken as tea or stewed for other means of consumption. However, do you know how much ginseng should be eaten? When to eat it? Who should not eat ginseng? This article will answer these questions.
Ginseng reigns "supreme" in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)—tagged as "the genie among the thousand herbs, the talisman of a hundred medicines." The earliest surviving work on TCM, "Shen Nong's Materia Medica" records the six major efficacies of ginseng, including supplementing the energy of internal organs, stabilizing the mood, improving heart palpitations, enhancing vision, and increasing cognition and memory. Consumption on a long-term basis was said to help bring longevity.
Ancient Chinese believed that ginseng was the genie from the earth, so it was also called "land essence" or "earth spirit." Ming dynasty physician Li Shizhen's "Compendium of Materia Medica" cites such a story. During the reign of Emperor Wen of the Sui Dynasty in China (AD 581-604), a man often heard cries every night from behind his house, but he could not find anyone there. Later, the man discovered a plant with unusually lush branches and leaves about one li (about 500 meters) behind his house. He then dug in the ground and found a piece of ginseng, which was shaped like a human with complete limbs. After that, he did not hear the strange cries anymore.
Nature, Flavors, Meridian Tropism, and Use
TCM believes that each medicine has a specific nature, flavor, and corresponding attributed meridians, and ginseng is no exception. Ginseng tastes sweet and slightly bitter, and when used raw, it is "neutral" by nature—that is, it has a mild medicinal property. And when used when ripe, it is slightly "warm" in nature and has a certain effect of nourishing vitality. TCM refers to the energy in the human body as "qi," and "native qi" refers to the natural driving force of all human physiological activities.
TCM believes that the human body has a "meridian" system through which energy flows from the internal organs throughout the body. In this respect, ginseng mainly follows the heart, lung, spleen, and kidney meridians, with a minor portion of it in the liver meridian, and has curative effects on all these organs and parts along its paths.
According to relevant TCM records, ginseng mainly treats symptoms of profuse sweating, severe vomiting and diarrhea, massive blood loss, loose stools, fatigue, frailty, prolapse of the anus, and visceral sagging caused by prolonged dissipation of vitality.
Six Benefits of Ginseng on the Human Body

Six benefits of ginseng on the human body.
So, how does modern medicine explain the efficacy of ginseng?
1. Regulates the central nervous system
Ginseng can regulate nerve function, improve cognitive ability and efficiency, help fight fatigue, and improve neurasthenia and vascular headache.
2. Improves the cardiovascular system
Ginseng can invigorate the heart, and improve weak heartbeat and arrhythmia.
Studies have found that ginsenosides have multiple effects on cardiovascular function, including regulating blood pressure and blood lipids and protecting vascular endothelial cells.
Ginseng can dilate blood vessels and improve blood circulation. Therefore, if a stroke patient has symptoms of limb stiffness and physical discomfort, and is of deficiency in constitution, that is, weak body and insufficient blood, ginseng can be used to improve the blood circulation within the heart and its surrounding blood vessels.
In addition, ginseng has an anti-shock effect, which can significantly strengthen the heartbeat, so it is particularly effective for hemorrhagic shock and acute toxic shock.
3. Enhances body adaptability
Ginseng can change the adaptability of the body and enhance the body's defense against harmful substances. It is suitable for hyperglycemia caused by uncontrolled diet, hypoglycemia caused by insulin, and myocardial infarction complications from cardiogenic shock.
4. Activates the endocrine system
Studies have found that ginseng can activate the pituitary gland and adrenal cortex system, promote the secretion of corticosteroids, and enhance the body's ability to resist stress.
Studies have also found that ginsenosides have similar effects as sex hormones, are suitable for sexual dysfunction diseases, and can also improve menopausal symptoms.
5. Regulates metabolismGinseng can promote protein synthesis and the division of bone marrow cells and also has a synergistic effect on lowering blood sugar and insulin. It can also promote lipid metabolism, lower cholesterol, and prevent atherosclerosis.
6. Anti-tumorGinseng also has a beneficial effect on gastric, intestinal, and other cancers. Studies have shown that ginsenosides in ginseng can inhibit cancer cell metastasis, inhibit angiogenesis and tumor growth, and induce cancer cell apoptosis.
Effect of Processing on Efficacy
Ginseng can also be classified according to its way of processing, and there are three categories: "dried fresh ginseng," "red ginseng," and "sugary ginseng."
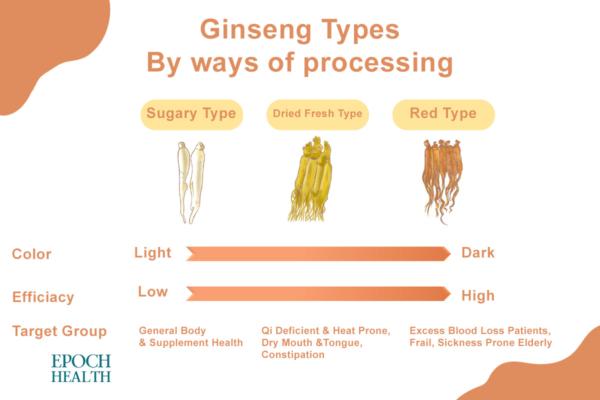
Different processing methods of ginseng affect its efficacy.
Dried fresh ginseng means that after the ginseng is harvested, it is dried under the sun or roasted dry. Dried fresh ginseng retains its efficacy because it does not go through any artificial steaming or heating process, so its effective ingredients remain relatively intact. However, because the enzyme has not been destroyed by high temperature, the active ingredient of ginseng, namely the ginsenoside, is easily hydrolyzed by the enzyme at a certain temperature and humidity. Therefore, this type of ginseng is not easy to keep for a long time.
The ginseng most commonly used is red ginseng, which is the result of fresh ginseng having been steamed for 3 to 4 hours inside a steam oven, then dried under the sun or roast dried, with the roots and fibrous roots removed afterward. During the steaming process, some of its ginsenosides will be lost, but due to this high-temperature cooking, the enzyme loses much of its activity, so its ginsenosides are not easily hydrolyzed during storage and have a much better shelf life.
Sugary ginseng is fresh ginseng dipped in boiling water for a while, then taken out and soaked in white sugar for about 20 hours. After the syrup is rinsed off, it is then dried under the sun or by roasting. It is called white ginseng at this stage. When white ginseng is punctured and infused with sugar, it transforms into sugary ginseng. Because of its high sugar content and that it is usually made from lower-quality ginseng, sugary ginseng's overall quality is considered the lowest among the three types.
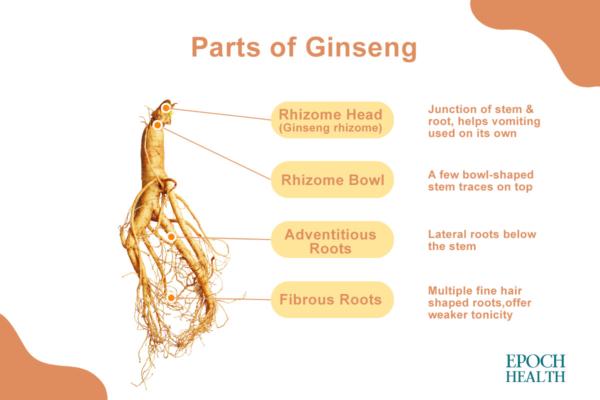
The fibrous root of ginseng, usually called "ginseng root," can also be used for medicinal purposes, however, with relatively weaker tonicity. In addition, the junction of the stem and root is called "rhizome head" or "ginseng rhizome," which can be used as a medicine on its own and has the effect of inducing vomiting.
Different parts of ginseng.
TCM believes that both food and medicinal herbs have four different properties: warm, hot, cold, and cool. Warm and hot food will make people feel warm, but eating too much of it will also make people feel dry, irritable, and hot, so it is more suited for people with cold physiques. On the other hand, cool and cold food has a chilling effect and is suitable for people with hot and dry constitutions. But those who are easily sickened by coldness should not eat too much cold and cool food. Neutral food (neither hot nor cold) is suitable for everyone.
The processing method of ginseng can also affect its properties. Because fresh sun-dried ginseng is not processed with heat, its medicinal properties remain relatively neutral and slightly cold. Red ginseng has been treated with heat, and its medicinal properties will turn slightly warmer.
Use of Ginseng as a Tonic and Its Proper Dosage
In general, as a tonic, ginseng should not be used excessively, otherwise it can lead to symptoms called ginseng poisoning that usually manifest as high blood pressure, hyperaesthesia, insomnia, irritability, itchy skin, skin rashes, and even precocious puberty in children.

Excessive use of ginseng may cause the above symptoms.
The following is the recommended general dosage. If you experience adverse effects after taking ginseng, it is recommended to consult a TCM practitioner.
1. For extreme exhaustion
Ginseng can be used to rescue critically ill patients with extreme exhaustion. Generally, 15 to 30 grams (0.53 to 1.1 ounces) are used, made into a thick decoction.
2. As a supplement
From the TCM perspective, those with a weak or cold type of constitution can take red ginseng. They can take it once every 5 to 7 days but always avoid excess. In this way, it will be a more stable and safer way to slowly fill up the energy of the body.
Method: When preparing with water, typically use 5 to 10 grams (0.18 to 0.35 ounces) of ginseng for decoction. If using ginseng powder, a dosage of 1.5 to 3 grams (0.05 to 0.1 ounce) can be taken with warm water.
Symptoms of Ginseng Poisoning and Treatment
For alleviating symptoms of ginseng poisoning, a simple remedy is to eat about 30 grams (1 ounce) radish seeds. Alternatively, you can also eat half or one whole white radish directly and decoct it for consumption.
Therefore, when you need to eat ginseng as a tonic, you should not eat radishes, so as not to reduce the tonicity of ginseng.
3 Dietary Therapeutic Options of Ginseng
In addition to the above methods, ginseng can also be used therapeutically in the diet:
1. Ginseng tea
Cut 3 to 5 grams (0.1 to 0.17 ounce) ginseng into thin slices and steep in hot water (200 ml) for half an hour to make ginseng tea. Drink this ginseng tea regularly. Along with drinking the tea, you can eat the steeped ginseng slices. Once their flavor becomes lighter after steeping, chew them slowly before swallowing. This kind of tea is very suitable for patients with chronic diseases, or those who are frail and sick.
2. Keep ginseng slices in the mouth
Cut ginseng into thin slices (3 to 5 grams), take 2 to 3 slices at a time, keep them in the mouth, chewing slowly and thoroughly, then swallow. For people who usually need a tonic to strengthen their body and eliminate fatigue, this method is extremely easy to work with.
3. Ginseng chicken soup
Ingredients:
3 to 9 grams (0.1 to 0.3 ounce) of ginseng slices
a spring chicken
1000 ml (33 ounces) water
Preparation
Stew for 1 to 2 hours, until the chicken is cooked and softened.
The whole portion can be consumed in 2 to 3 separate servings.This soup is suitable for people suffering much postoperative blood loss, or those who are frail and need to be recuperated after surgery. If it is used as a daily health care medicinal diet, the dosage of ginseng should be reduced by half.
Taboos for Eating Ginseng

Six groups of people should take ginseng with caution.
1. Excessive heat type
TCM believes that too much heat or fire in the body can lead to disease. TCM divides the heat of the human body into two categories—"virtual" heat, and "real" heat. Virtual heat is heat caused by body fluid damage, while real heat is heat caused by external forces, such as eating too much spicy, grilled, fried food, or hot weather. Eating ginseng is not suitable for people with real heat symptoms which include red face and hot body, constipation, high blood pressure, edema, oliguria, insomnia, and irritability.
In addition, it is not suitable to eat ginseng if you have a cold and fever, during the summer season, or when in a state of irritability. Those with abdominal distension, abdominal pain, or acute diarrhea, should not take ginseng.
2. Bipolar disorder patients
Most patients with manic disorder and bipolar disorder belong to the constitution of real heat syndrome. Taking ginseng may cause further discomfort symptoms such as headache and mania.
3. Those who are prone to excitement and insomnia
People who are prone to excitability and insomnia should avoid taking ginseng before going to bed. Because of the qi-tonifying effect of ginseng, it may cause hyperactivity and make falling asleep difficult.
It is best to take ginseng within an hour before or after a meal in the morning, and it is not recommended to take it after noon.
4. Children and pregnant women
Use only under the care of a qualified health care provider.
6. Breastfeeding women
Breastfeeding mothers should not eat ginseng as it can cause milk glands to shrink.
Note: The Chinese medicinals mentioned in this article are generally available in Chinese supermarkets or Chinese medicine stores. Please consult a professional physician for specific treatment plans and prescriptions.
No comments:
Post a Comment