What this makes rather clear is that the cost benefit equatioin for vaccination is not that complelling. Adding additional shingle victims makes it far worse.
I have had childhood chicken pox and the course of the disease was mild and equivalent to a nasty cold that sets you back for several days. I have never contracted shingles which is a real risk in my case.
Yet the purpose of vaccination is to drive the virus into extinction. Why is this not happening? Has occurrences of this disease actually plummeted? All vaccine protocols need to have these types of meta stats. Granted, some diseases cannot be driven into extinction as wild reservoirs exist. It is also true that those chronic childhood diseases appear to be hugely suppressed.
The industry has been doing an awful job of presenting their case. Why?
..
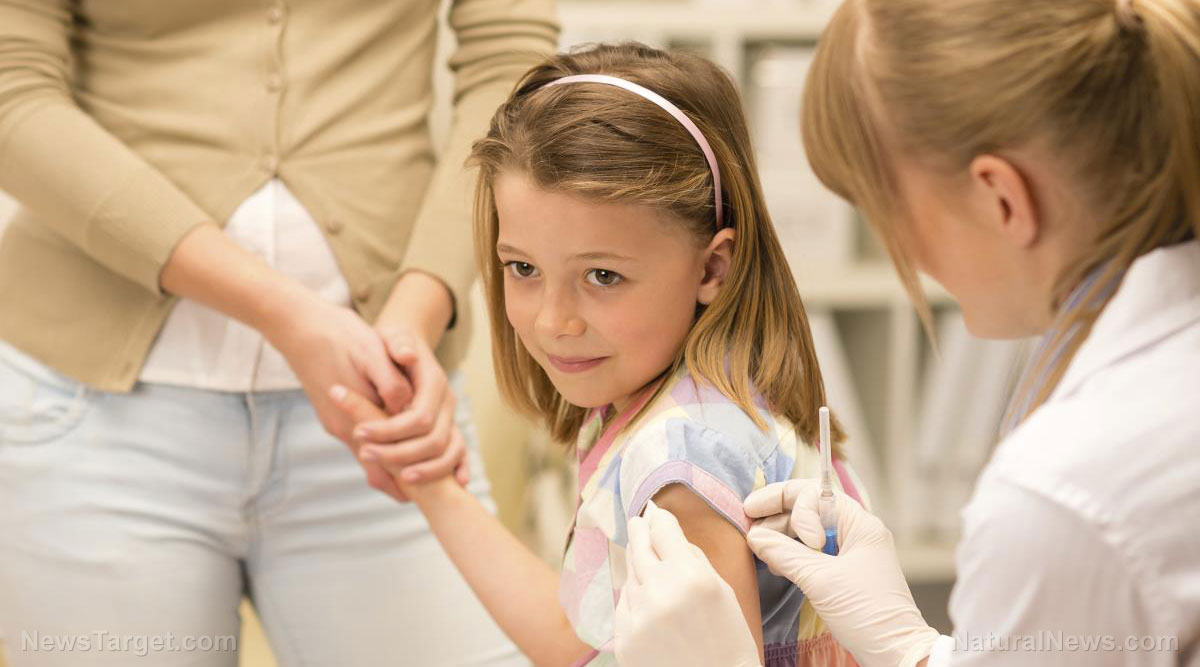
Vaccinating against chickenpox often causes shingles, even in children
Friday, February 08, 2019 by: Jessica Dolores
Tags: badhealth, badmedicine, Big Pharma, chicken pox, Dangerous Medicine, shingles, shots, skin rash, vaccination, vaccine, vaccine damage, vaccine injury
(Natural News) Like all diseases, chickenpox takes a lot of joy out of childhood. When he gets it, he can’t learn more at school, enjoy the sunshine, or even explore the great outdoors.
However, if you think that getting a shot for chickenpox solves the problem, think again. According to researchers from Harvard Medical School, healthy children who were vaccinated for chickenpox developed shingles soon after. The study, published in the journal Pediatric Dermatology, looked at case studies of shingles that were first thought to be skin rashes.
Friday, February 08, 2019 by: Jessica Dolores
Tags: badhealth, badmedicine, Big Pharma, chicken pox, Dangerous Medicine, shingles, shots, skin rash, vaccination, vaccine, vaccine damage, vaccine injury
(Natural News) Like all diseases, chickenpox takes a lot of joy out of childhood. When he gets it, he can’t learn more at school, enjoy the sunshine, or even explore the great outdoors.
However, if you think that getting a shot for chickenpox solves the problem, think again. According to researchers from Harvard Medical School, healthy children who were vaccinated for chickenpox developed shingles soon after. The study, published in the journal Pediatric Dermatology, looked at case studies of shingles that were first thought to be skin rashes.
Shingles and chickenpox are cut from the same cloth
Both shingles and chickenpox come from the varicella-zoster virus. When a person first comes in contact with the virus, usually by touching or breathing it in, it results to “itchy, fluid-filled blisters” that result to scabs – the common symptoms of chickenpox.
A person with chickenpox will experience headaches and fevers, feel tired, and lose his appetite as a result of the condition, which usually lasts from five to seven days.
Some parents consider vaccines to prevent their children from the condition; however, this does not guarantee that they are completely protected. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, people who have been vaccinated may still get chickenpox. In some cases, it may develop to be as serious as those without vaccination.
After having chickenpox, the virus “hibernates” in nerve tissue near the spinal cord and the brain. While the reasons for the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus are still unclear, it can reactivate and travel along nerve pathways to the skin – this is the onset of shingles.
There are similarities between shingles and chickenpox: Rashes develop in the skin, together with fluid-filled blisters and itching. However, people with shingles experience pain, numbness, or tingling in their skin. They can also feel fatigued and have increased sensitivity to light.
For the study, the authors looked at seven cases of children who contracted herpes zoster (shingles) at the site of their varicella-zoster (chickenpox) vaccination. The chickenpox virus is known to lay dormant in a person and can reactivate as shingles. The researchers found the following symptoms as they scoured the cases. Most reports included lesions along with various kinds of skin abnormalities. Some children reported having a low-grade fever, while others had upper respiratory symptoms and joint pain. All children underwent diagnostic tests, and all of them recovered from shingles without any complications.
According to the researchers, the study underscored the outcomes of herpes zoster in vaccinated children, in particular, its clinical, diagnostic, and therapeutic effects. In particular, it highlighted the value of recognizing the symptoms of shingles in immunized children. “Shingles in healthy immunized children is rare, but when it occurs it may correlate to the original vaccination site,” concluded Dr.?Jennifer Huang, the study’s corresponding author. “Recognizing vaccine-associated shingles may prevent unnecessary procedures or testing.”
Managing shingles naturally
Having shingles is not a pleasant experience – you’re itchy all over, you feel weak and lethargic, and simply moving becomes such a painful chore. Instead of curling up in bed or popping an antiviral to treat shingles, here are some things you can do to help alleviate the condition.
Taking a cool shower is known to soothe skin and ease the pain and itchiness that come with blisters. For maximum effect, go for a healing bath to reduce symptoms. Pour one to two cups of colloidal oatmeal or cornstarch into a lukewarm bath for 15 to 20 minutes.
A quick fix is to apply a cool, moist compress to the area that itches to relieve the symptoms. Stick with a cool compress, though – an ice pack increases skin sensitivity and makes it worse.
A mixture made of cornstarch, baking soda, and water is also a great way to get rid of skin rashes. Apply the paste to the affected area, let it sit for 15 to 20 minutes, and rinse.
Need more proof that vaccines are nothing but trouble? Follow Immunization.news to learn more.
Sources include:
Science.news
ScienceDaily.com
MayoClinic.org
CDC.gov
Healthline.com
No comments:
Post a Comment